FED-STD-791D
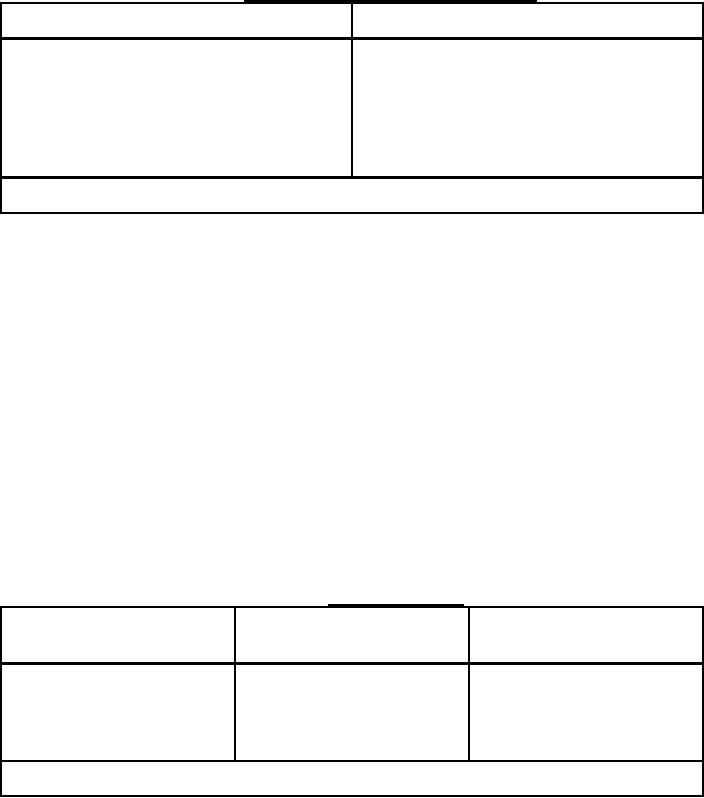
TABLE I. Size ranges and counting magnifications.
Particle size range (largest dimension), Ķm
Counting magnifications, diameters
5 to 15
100
15 to 25
100
25 to 50
100
50 to 100
100
Over 100 1 (length-wide ratio under 10:1)
45
Over 100 1 (length-wide ratio over 10:1)
45
1 Fibers.
6.10 For each size range, determine sampling area and calibration factor on the basis of
the estimate. If the estimated number of particles of that size was 5000 or less, use sampling
area and factor shown in Table II. If the estimated number was more than 5000, determine area
and factor as follows:
6.10.1 Select a sampling area consisting of at least 10 sections (chosen at random), each
of which is one grid length long (0.308 cm), and narrow enough to contain no more than 50
particles (of that size range under consideration). (See Figure 1.)
6.10.2 Using the micrometer eyepiece, measure the width of each unit area, and
determine the sum or the widths. Compute the calibration factor (see 7.1).
6.11 For each size range, count the particles within the sampling area, using the counting
magnification specified in Table I. (See Figure 2). Include in the tally those particles lying on
the upper and left boundary lines of the area as well as those within the areas selected. (Particles
on the lower and right boundary lines are tallied with those in the square below or to the right.)
TABLE II. Calibration factors
Estimated number of
Sampling area
Calibration factor
particles
1 to 50
100 squares (total area)
1
51 to 1000
20 squares (at random)
5
1001 to 5000
10 squares (at random)
10
10 sections 1
More than 5000
1 See paragraph 6.10.
7. CALCULATIONS
7.1 Compute calibration factor:
89
For Parts Inquires call Parts Hangar, Inc (727) 493-0744
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business