FED-STD-791D
distance from reference mark to each peak. Compare with those obtained from the
standard acid scan and identify each recovered acid accordingly.
6.16 Quantitative determination of the recovered acids ≠ On the chromatogram of
the standard acid mixture , draw a base line from the reference mark to that point on the
scan which indicates the C10 acid has been eluted completely. From the base line
measure each peak height in mm and sum all peak heights. Normalize each peak height
by dividing each by the sum of the heights. Establish a correction factor for each acid by
dividing the normalized peak height per mole of C5 acid by the normalized peak height
per mole of each component acid. On the chromatogram of the recovered acids, proceed
as above up to and including the normalization of each peak height. Multiply the
normalized peak height of each acid component by its appropriate correction factor to
obtain a "corrected" height for each. To obtain the mole-percent of each acid, divide the
"corrected" peak height of each by the sum of all the "corrected" heights times 100.
Record each component to the nearest integral value. Examples of the illustrated in
Table 1 and 2.
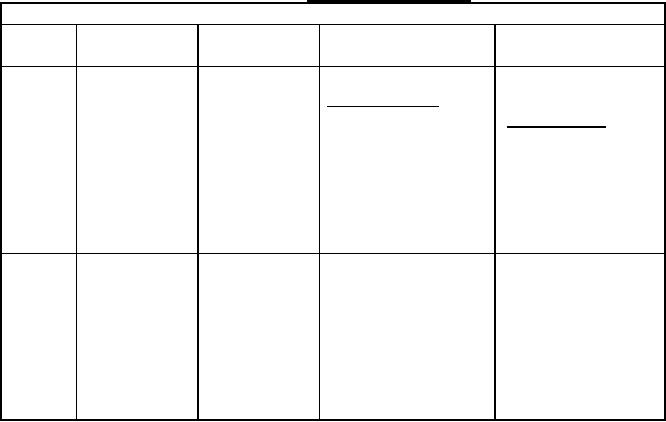
TABLE 1. Standard acid mixture.
Chromatographic retention times and correction factors
Acid
Retention
Peak height
Normalized peak area Correction factor
time
(see 6.3.1)
Peak height of
Normalized peak
one component
Height of C5
Sum of peak heights
acid per mole
Of all components
normalized peak
height of component
acid per mole
in mm
In mm
(measured)
(measured)
C4
70
168
11.6
1.14
Iso-C5
74
187
12.9
1.02
C6
84
192
13.2
1.00
C7
98
182
12.6
1.05
C8
115
155
10.7
1.23
C9
136
212
14.6
1.36
C10
162
169
11.7
1.69
196
184
12.7
2.08
239
For Parts Inquires call Parts Hangar, Inc (727) 493-0744
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business